I. Introduction
In a world where health and wellness have become paramount, one aspect that often goes overlooked is the strength and vitality of our lungs. These vital organs play a silent yet crucial role in our daily lives, providing the oxygen our bodies need to function efficiently. The significance of lung health cannot be overstated, and in this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of how to make your lungs strong.
Table of Contents
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
II. Anatomy of the Lungs
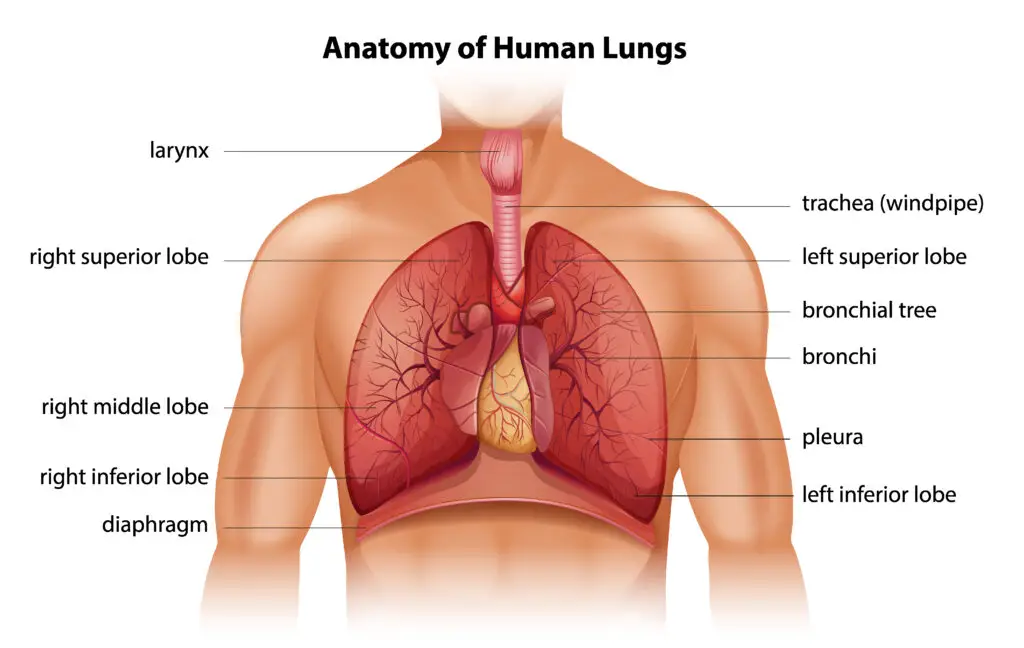
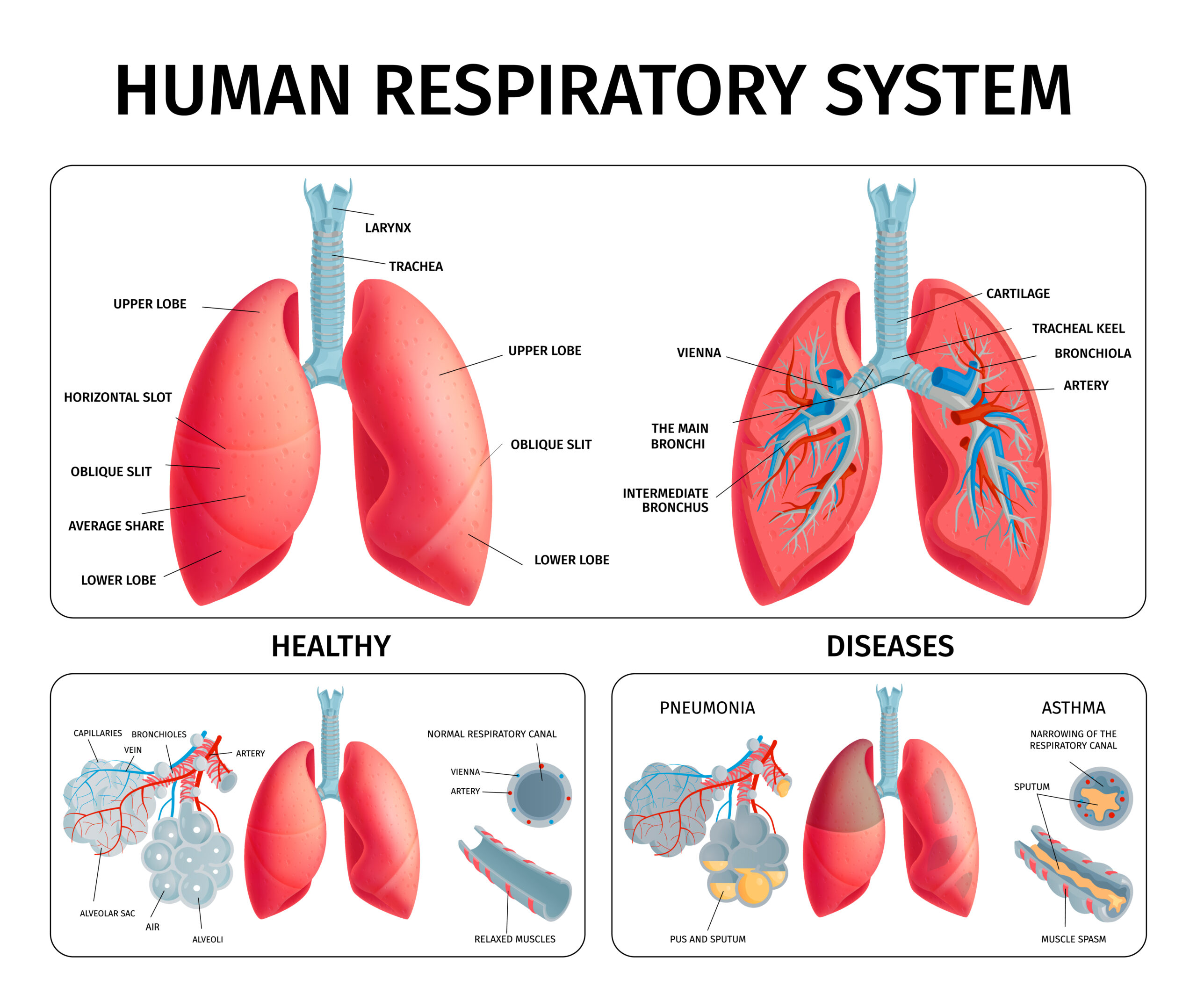
To truly understand how to strengthen your lungs, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental anatomy of these respiratory powerhouses. The respiratory system consists of a complex network of structures, including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and the alveoli. Let’s delve into these components to appreciate how they work together seamlessly to support your respiratory needs.
The trachea, often referred to as the windpipe, serves as the main airway that connects your throat to your lungs. It is a sturdy tube composed of cartilage rings, ensuring it remains open even during exhalation.
Bronchi, on the other hand, are the two primary branches that extend from the trachea, with one entering each lung. These bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles, which resemble a branching tree. The bronchioles eventually lead to tiny air sacs known as alveoli.
Alveoli are the workhorses of the respiratory system. These small, grape-like clusters of air sacs are where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. The walls of the tiny air sacs called alveoli are extremely thin, which enables a highly effective exchange of gases between the lungs and the blood vessels.
The network of blood vessels surrounding the alveoli is equally crucial. These vessels transport oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart, which then pumps it to every cell in the body. Understanding this intricate system sets the stage for exploring how to maintain and enhance lung health.
III. Common Lung Problems
Before we delve into strengthening our lungs, it’s essential to recognize the various challenges and conditions that can compromise their function. Some of the most prevalent lung problems include:
A. Asthma: A Chronic Inflammatory Condition
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflamed airways. This inflammation can lead to narrowed air passages, causing symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing.
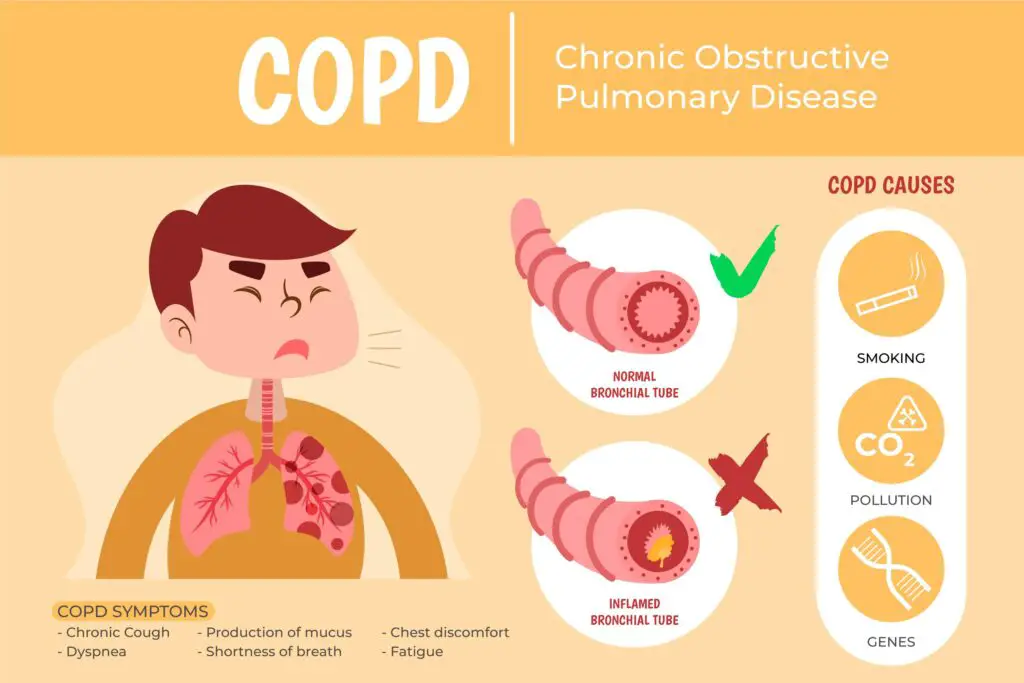
B. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a general term that includes both chronic bronchitis and emphysema, two specific lung conditions. It is often caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, such as cigarette smoke. COPD progressively limits airflow, leading to symptoms like chronic cough, excessive mucus production, and breathlessness.
C. Pneumonia: Infections in the Lung
Pneumonia is an infection that can impact either a single lung or both of them. Frequently, this condition is triggered by bacteria, viruses, or other tiny organisms. Symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
D. Lung Cancer: A Deadly Threat
Lung cancer is a malignant growth in the lungs, typically linked to tobacco smoking. It ranks among the primary reasons for cancer-related fatalities on a global scale.
Understanding these common lung problems underscores the importance of proactively working to maintain lung health.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
IV. Lifestyle Factors Affecting Lung Health
The state of your lungs is significantly influenced by the choices you make in your daily life. Several lifestyle factors can either strengthen or weaken your respiratory system. Let’s explore these factors and how they impact your lung health.
A. The Impact of Smoking on Lung Function
Smoking remains the single most detrimental behavior for lung health. Cigarette smoke contains thousands of harmful chemicals, many of which can damage the delicate tissues of the respiratory system.
The tar in cigarette smoke, for example, can accumulate in the lungs, leading to chronic inflammation and a higher risk of lung cancer. Nicotine, a highly addictive substance in cigarettes, constricts blood vessels, making it harder for the lungs to receive oxygen.
B. Secondhand Smoke: A Silent Danger
Even if you don’t smoke, exposure to secondhand smoke can be detrimental. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals as direct smoke and can harm the lungs of those who inhale it, especially children and non-smoking adults.
C. Nutrition and Lung Health
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining lung health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support lung function. Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, help protect the lungs from oxidative stress.
D. Physical Activity and Lung Strength
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for lung health. Cardiovascular exercises, in particular, help improve lung capacity by increasing the efficiency of oxygen exchange. Engaging in activities like running, swimming, or cycling can lead to stronger lungs over time.
E. The Importance of Hydration
Staying properly hydrated is essential for maintaining optimal lung function. Adequate hydration keeps the mucus lining in the airways thin, facilitating the removal of irritants and pathogens. It also helps maintain the elasticity of lung tissues, ensuring they can expand and contract efficiently during breathing.
As we move forward in our journey to stronger lungs, it’s crucial to acknowledge the profound impact these lifestyle factors can have on our respiratory well-being. Making informed choices can pave the way to healthier, more robust lungs.
V. Breathing Techniques for Strong Lungs
One of the most direct ways to improve lung strength and function is by mastering various breathing techniques. Proper breathing not only maximizes oxygen intake but also ensures that the respiratory muscles are functioning optimally.
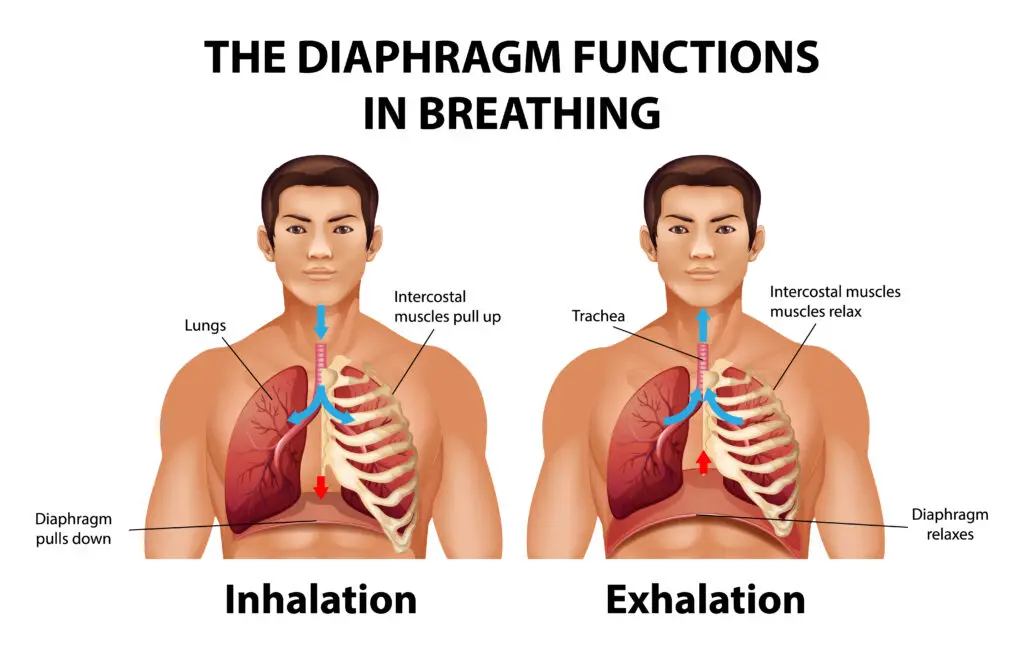
A. Diaphragmatic Breathing: The Foundation
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as abdominal or deep breathing, forms the foundation of effective respiration. This technique involves the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle located just below the lungs.
To practice diaphragmatic breathing:
- Look for a cozy and peaceful spot to either sit or lie down.
- Place your hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen.
- Take a deep breath in through your nose, letting your belly expand as your lungs fill with air.
- Exhale slowly through pursed lips, feeling your abdomen fall as you release the air.
This technique encourages the use of the diaphragm, allowing for deeper and more efficient breathing. Regular practice can enhance lung capacity and oxygenation.
B. Pursed Lip Breathing: Enhancing Lung Efficiency
Pursed lip breathing is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic lung conditions like COPD. This technique helps to slow down the breathing rate and improve the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
To practice pursed lip breathing:
- Sit in a comfortable position.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for two counts.
- Exhale gently through pursed lips for four counts, as if you’re blowing out a candle.
- Repeat this cycle several times.
Pursed lip breathing promotes more thorough exhalation, preventing the trapping of stale air in the lungs and ensuring a better supply of fresh oxygen.
C. Pranayama: Yogic Breathing Techniques
The ancient practice of pranayama from yoga offers a wide array of breathing techniques that not only enhance lung strength but also promote mental clarity and relaxation. Here are a few pranayama techniques to consider:
- Kapalbhati Pranayama: This rapid, forceful exhalation technique helps clear the respiratory passages and improve lung capacity.
- Anulom Vilom: Also known as alternate nostril breathing, this technique balances the flow of energy in the body and enhances oxygenation.
- Bhastrika Pranayama: Bhastrika involves rapid and forceful inhalation and exhalation, increasing the supply of oxygen to the body.
D. Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT)
Inspiratory muscle training focuses on strengthening the muscles responsible for inhalation. Devices like the inspiratory muscle trainer create resistance during inhalation, making the respiratory muscles work harder.
Consistent use of IMT devices can lead to increased lung capacity and improved breathing endurance, particularly in athletes and individuals with respiratory conditions.
Mastering these breathing techniques can empower you to take control of your lung health. Whether you’re an athlete looking to enhance performance or someone seeking relief from a chronic lung condition, these techniques offer valuable tools for improving lung strength.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
VI. Exercise and Lung Health
Exercise is a powerful tool for improving lung health. Engaging in regular physical activity not only enhances cardiovascular fitness but also strengthens the respiratory muscles. Let’s explore the various types of exercises that can contribute to stronger lungs.
A. Cardiovascular Exercises: A Boost for Lungs
Cardiovascular or aerobic exercises are among the most effective ways to increase lung capacity and strengthen the heart. These exercises elevate the heart rate and breathing rate, promoting the efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
Some excellent cardiovascular exercises for lung health include:
- Running: This high-intensity exercise challenges the lungs and improves lung capacity.
- Cycling: Whether indoors or outdoors, cycling enhances cardiovascular endurance and lung function.
- Swimming: Swimming engages both the upper and lower body, promoting deep breathing and lung expansion.
- Jumping Rope: This simple yet effective exercise can quickly elevate your heart rate and challenge your lungs.
Consistency is key when incorporating cardiovascular exercises into your routine. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of these activities can lead to notable improvements in lung strength over time.
B. Strength Training for Respiratory Muscles
While cardiovascular exercises focus on overall fitness, strength training targets specific muscle groups, including those involved in respiration. A strong diaphragm and intercostal muscles (between the ribs) are essential for efficient breathing.
Incorporate the following exercises to strengthen your respiratory muscles:
- Diaphragmatic Strengthening Exercises: These exercises focus on contracting and relaxing the diaphragm. For example, you can perform deep abdominal breathing exercises while lying on your back.
- Intercostal Muscle Strengthening: Exercises like the “ribcage stretch” can help stretch and strengthen the intercostal muscles, improving their flexibility and function.
Strength training not only enhances lung function but also contributes to overall respiratory well-being.
C. Yoga and Pilates: A Holistic Approach
Yoga and Pilates are holistic exercise disciplines that emphasize controlled movements, flexibility, and mindful breathing. These practices not only enhance lung strength but also promote relaxation and stress reduction.
Incorporate the following yoga poses and Pilates exercises to improve lung function:
- Yoga Poses: Poses such as the Cobra, Cat-Cow, and Bridge Pose encourage deep breathing and lung expansion.
- Pilates Exercises: Pilates movements, especially those targeting the core and chest, can strengthen the muscles involved in respiration.
The combination of physical activity and controlled breathing in yoga and Pilates offers a well-rounded approach to lung health.
D. Sports and Lung Performance
If you’re an athlete or sports enthusiast, you may be particularly interested in optimizing your lung performance. Different sports require varying levels of lung capacity and endurance.
- Endurance Sports: Activities like long-distance running, cycling, and swimming demand high levels of lung capacity and efficient oxygen utilization.
- Strength Sports: While strength sports like weightlifting may not focus solely on lung capacity, overall cardiovascular fitness can still benefit performance.
- Combat Sports: Martial arts and combat sports often require rapid, controlled breathing during intense physical exertion.
Tailoring your exercise routine to align with your specific athletic goals can help you achieve peak lung performance.
VII. Air Quality and Lung Health
The quality of the air you breathe can significantly impact your lung health. Both indoor and outdoor environments can expose you to pollutants and irritants that can compromise your respiratory well-being. Understanding and addressing air quality issues is crucial for maintaining strong lungs.
A. Indoor Air Quality: Tips for Improvement
Many people spend a significant portion of their time indoors, making indoor air quality paramount. Here are some steps to improve indoor air quality:
- Ventilation: Make sure your home has good airflow by opening windows and using exhaust fans when needed.
- Air Purifiers: Think about using air purifiers that have HEPA filters to get rid of particles and allergens from the air.
- Humidity Control: Maintain optimal humidity levels to prevent the growth of mold and dust mites.
- Reduce Smoking: If you or someone in your household smokes, make efforts to quit or limit smoking indoors.
Taking these measures can help create a healthier indoor environment that supports lung health.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
B. Outdoor Air Pollution: Minimizing Exposure
Outdoor air pollution, often caused by vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and natural sources, can have a detrimental impact on your lungs. While you may not have control over outdoor air quality, you can take steps to minimize your exposure:
- Check Air Quality Index (AQI): Stay informed about air quality in your area by checking the AQI regularly. Reduce the time you spend outside on days when the air has high pollution levels.
- Use Masks: In highly polluted areas or during wildfire seasons, wearing masks that filter out fine particulate matter can provide some protection.
- Limit Outdoor Exposure: When pollution levels are high, consider staying indoors or relocating to cleaner areas for exercise and recreation.
Being mindful of outdoor air quality and taking appropriate precautions can reduce your risk of respiratory issues associated with pollution.
C. Occupational Hazards: Protecting Your Lungs
For individuals working in specific industries, occupational hazards may pose a significant risk to lung health. These hazards can include exposure to dust, chemicals, and airborne contaminants. Protective measures in the workplace are essential to safeguard lung health:
- Use Respiratory Protective Equipment: When working in environments with airborne hazards, wear appropriate respiratory protection, such as masks or respirators.
- Follow Safety Guidelines: Adhere to workplace safety guidelines and protocols to minimize exposure to lung irritants.
- Regular Health Checks: If your occupation poses lung health risks, undergo regular health assessments to monitor your respiratory function.
By taking precautions and advocating for your safety in the workplace, you can protect your lungs from potential harm.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
VIII. Natural Remedies for Lung Health
In addition to lifestyle choices and physical activity, natural remedies and alternative therapies can complement your efforts to maintain strong lungs. While these approaches should not replace medical treatment when needed, they can be valuable adjuncts to support respiratory well-being.
A. Herbal Remedies and Supplements
Certain herbs and supplements have been associated with lung health benefits. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating these remedies into your routine, as they can interact with medications and have side effects.
- Eucalyptus: Eucalyptus oil or leaves are often used in steam inhalation to help clear airways.
- Ginger: Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties and may provide relief from respiratory symptoms.
- Turmeric: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit lung health.
Supplements such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and quercetin have also been studied for their potential lung health benefits.
B. The Healing Power of Steam Inhalation
Steam inhalation is a time-tested remedy for respiratory congestion and irritation. It involves inhaling warm, moist air infused with beneficial substances like essential oils or herbs. Steam inhalation can help:
- Clear Mucus: Inhaling steam can help loosen and clear mucus from the airways.
- Soothe Irritation: Steam can provide relief from throat and airway irritation.
- Open Airways: The warmth of steam can relax airway muscles and improve breathing.
To practice steam inhalation:
- Boil water in a pot and remove it from the heat source.
- Add a few drops of essential oil or herbs like eucalyptus or peppermint.
- Bend over the pot and drape a towel over your head to capture the steam.
- Inhale the steam for 10-15 minutes, taking care not to get too close to the hot water.
C. Salt Therapy (Halotherapy)
Salt therapy, also known as halotherapy, involves exposure to aerosolized salt particles in a controlled environment. This therapy is often used to alleviate respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. The salt particles are believed to:
- Reduce Inflammation: Salt is naturally anti-inflammatory and may help reduce airway inflammation.
- Loosen Mucus: Salt particles can thin mucus, making it easier to clear from the airways.
- Improve Lung Function: Halotherapy may enhance lung function by promoting better oxygenation.
Salt therapy can be administered in specialized salt rooms or through portable devices designed for home use.
D. Aromatherapy for Respiratory Wellness
Aromatherapy involves the use of essential oils to promote physical and emotional well-being. Several essential oils are known for their respiratory benefits:
- Eucalyptus Oil: Eucalyptus oil is commonly used to ease congestion and improve breathing.
- Peppermint Oil: Peppermint oil has a cooling effect and can help open airways.
- Lavender Oil: Lavender oil promotes relaxation and can reduce stress-related breathing issues.
Aromatherapy can be enjoyed through diffusers, inhalers, or diluted essential oils applied topically.
IX. Medical Interventions
While lifestyle choices and natural remedies can significantly contribute to lung health, medical interventions may be necessary in cases of severe respiratory conditions. These interventions range from vaccinations and medications to oxygen therapy and surgical procedures.
A. Vaccinations for Respiratory Diseases
Vaccinations are a crucial preventive measure for various respiratory diseases. Some vaccines that protect against respiratory infections include:
- Influenza (Flu) Vaccine: An annual flu shot can help prevent seasonal influenza, which can lead to respiratory complications.
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: This vaccine protects against pneumococcal infections, including pneumonia and certain types of meningitis.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Vaccine: In regions with a high prevalence of TB, the TB vaccine may be recommended to prevent infection.
Vaccinations not only protect individuals but also contribute to community immunity, reducing the spread of contagious diseases.
B. Medications for Lung Health
Various medications are prescribed to manage respiratory conditions and support lung health:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax and expand the airways, making it easier for you to breathe. They are often used in conditions like asthma and COPD.
- Corticosteroids: Steroid medications can help reduce airway inflammation and are used in the treatment of asthma and other inflammatory lung diseases.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are prescribed to treat bacterial lung infections such as pneumonia.
- Antivirals: Antiviral medications may be used to treat viral respiratory infections like influenza.
- Mucolytics: Mucolytic drugs help break down and thin mucus, aiding in its removal from the airways.
It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding the use of medications and to adhere to prescribed treatment regimens.
C. Oxygen Therapy: A Lifesaver
In cases where lung function is severely compromised, oxygen therapy can be a life-saving intervention. Oxygen therapy involves delivering supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate blood oxygen levels. It is commonly used in conditions like:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Patients with severe COPD may require oxygen therapy to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Pneumonia: Severe cases of pneumonia can lead to oxygen depletion, necessitating oxygen therapy.
- Hypoxemia: Low blood oxygen levels, known as hypoxemia, can occur in various medical conditions and may require oxygen supplementation.
Oxygen therapy can be administered through nasal cannulas, masks, or specialized equipment tailored to individual needs.
D. Surgical Options for Severe Lung Conditions
In certain circumstances, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat severe lung conditions or correct structural abnormalities. Some common lung surgeries include:
- Lung Resection: This surgery involves the removal of a portion of a lung affected by cancer or other diseases.
- Lung Transplant: In cases of end-stage lung disease, a lung transplant may be considered.
- Bronchoplasty: This procedure is performed to repair or reconstruct damaged bronchi or airways.
- Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: In some cases of severe COPD, reducing the size of damaged lung tissue can improve breathing.
Surgical interventions are typically considered when other treatments have not yielded satisfactory results.

How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
X. Mind-Body Connection
The mind-body connection plays a significant role in lung health. Psychological and emotional factors can influence respiratory function and the perception of lung-related symptoms. Recognizing and addressing the emotional aspects of lung health is crucial for overall well-being.
A. Stress and Its Impact on Lung Function
Stress is a common trigger for respiratory symptoms. When stressed, the body often responds with shallow, rapid breathing, which can lead to feelings of breathlessness and anxiety. Chronic stress can also exacerbate conditions like asthma and COPD.
B. Mindfulness and Meditation for Respiratory Health
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can be invaluable for managing stress and improving lung health. These techniques promote relaxation and teach individuals to control their breathing and reduce anxiety.
C. Visualization Techniques
Visualization exercises can help individuals with lung conditions better manage their symptoms. Visualizing clear airways, relaxed breathing, and healthy lungs can have a positive impact on lung function and overall well-being.
D. Support Groups and Counseling
Coping with a long-term lung condition can be emotionally difficult. Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide a safe space to share experiences and learn coping strategies. Emotional support is a vital aspect of holistic lung care.
XI. Monitoring Your Lung Health
Monitoring your lung health is essential for early detection of any issues and for assessing the effectiveness of your efforts to strengthen your lungs. Regular check-ups and self-monitoring can provide valuable insights into your respiratory well-being.
A. The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for assessing lung function and identifying any potential problems. These visits may include:
- Spirometry: A lung function test that measures the amount and speed of air you can inhale and exhale.
- Chest X-rays: Imaging tests that can detect lung abnormalities, including tumors and infections.
- Blood Gas Analysis: A test that measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood.
Regular check-ups help detect lung issues early when they are more manageable.
B. Home Lung Function Tests
In addition to professional assessments, home lung function tests can provide ongoing monitoring and insight into your respiratory health. Some home tests include:
- Peak Flow Meter: A device that measures the force of your breath, helping you monitor changes in lung function.
- Pulse Oximeter: A tool that measures the oxygen saturation in your blood, indicating how well your lungs are delivering oxygen to your body.
- Spirometry at Home: Portable spirometers are available for home use, allowing you to track lung function over time.
Self-monitoring can help you track changes in lung function and provide data to share with your healthcare provider.
C. Keeping a Lung Health Journal
Maintaining a lung health journal can be a valuable tool for tracking symptoms, triggers, and lifestyle factors that may affect your respiratory well-being. In your journal, you can record:
- Daily symptoms and their severity
- Medications and treatments
- Exercise routines and their impact on breathing
- Environmental factors such as air quality
- Dietary choices and hydration
- Stress levels and emotional well-being
A lung health journal can help you identify patterns and make informed decisions about your lung care.
XII. Diet and Nutrition for Strong Lungs
Diet plays a pivotal role in overall health, including lung health. Proper nutrition provides the essential nutrients and antioxidants needed to support respiratory function and protect against lung-related conditions.
A. Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. Including foods rich in antioxidants in your diet can benefit lung health. Some antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants like vitamin C and flavonoids.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens contain antioxidants like vitamins A, C, and E.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are high in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamin E.
- Colorful Vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers provide a variety of antioxidants.
B. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Lung Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit lung health. These essential fats can help reduce airway inflammation and improve lung function.
C. The Role of Vitamins and Minerals
Certain vitamins and minerals are particularly important for lung health:
- Vitamin C: This antioxidant vitamin is known for its immune-boosting properties and its role in protecting lung tissues from damage.
- Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D levels are associated with improved lung function and a reduced risk of respiratory infections.
- Magnesium: Magnesium supports muscle relaxation, including the muscles involved in breathing.
- Selenium: Selenium is an essential mineral that may protect the lungs from oxidative stress.
A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can provide the nutrients your lungs need to stay strong.
D. Hydration: More Than Just Water
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining lung health. When you’re well-hydrated, the mucus lining in your airways remains thin and helps trap and remove irritants. Adequate hydration also supports overall bodily functions, including lung function.
While water is the primary source of hydration, herbal teas and certain fruits and vegetables with high water content can also contribute to your daily fluid intake.
As you embark on your journey to stronger lungs, consider adopting a balanced and nutritious diet that includes these lung-boosting foods and nutrients. What you eat can have a profound impact on your respiratory health.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
XIII. Smoking Cessation
If you are a smoker, one of the most powerful steps you can take to improve your lung health is to quit smoking. Smoking is the leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide and is responsible for numerous lung-related diseases and conditions.
A. The Road to Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is undoubtedly challenging, but it is also one of the most rewarding choices you can make for your lung health. The benefits of quitting begin almost immediately and continue to accumulate over time:
- Immediate Improvement: Within hours of quitting, your heart rate and blood pressure start to drop.
- Improved Lung Function: Over time, your lung function begins to improve, and the risk of lung cancer and respiratory infections decreases.
- Reduced Risk: The longer you remain smoke-free, the lower your risk of smoking-related diseases like COPD, heart disease, and stroke.
- Better Quality of Life: Quitting smoking leads to increased energy, improved sense of taste and smell, and enhanced overall well-being.
B. Support Systems for Smokers
Quitting smoking is often more successful with support. Several resources and strategies are available to help you quit:
- Nicotine Replacement Therapies: Products like nicotine gum, patches, and lozenges can help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
- Prescription Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications like varenicline or bupropion to aid in smoking cessation.
- Behavioral Counseling: Individual or group counseling sessions can provide strategies and coping mechanisms for quitting.
- Support Hotlines and Apps: Numerous hotlines and smartphone apps are designed to provide support and motivation throughout your quit journey.
Remember that quitting smoking is a process, and it may take multiple attempts before you succeed. Each attempt brings you one step closer to a smoke-free, healthier life.
XIV. Coping with Lung Diseases
Living with a lung disease can present unique challenges, both physically and emotionally. Coping with these conditions requires resilience, a strong support system, and strategies for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
A. Living with Asthma: Tips for Daily Life
Asthma is a long-term condition that needs continuous management. Here are some tips for individuals living with asthma:
- Medication Adherence: Take your prescribed asthma medications as directed by your healthcare provider, even when you’re feeling well.
- Allergen Avoidance: Identify and minimize exposure to allergens or triggers that worsen your asthma symptoms.
- Asthma Action Plan: Work with your healthcare provider to develop an asthma action plan that outlines steps to take in case of worsening symptoms.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor your lung function and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
B. Managing COPD: Strategies for Better Living
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive condition that requires proactive management. Consider the following strategies for managing COPD:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Make lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, staying active, and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Participate in pulmonary rehabilitation programs that offer exercise training, education, and emotional support.
- Oxygen Therapy: If prescribed, use oxygen therapy as directed to maintain adequate blood oxygen levels.
- Medication Management: Adhere to your medication regimen and discuss any side effects or concerns with your healthcare provider.
C. Lung Cancer Support
A lung cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but there are support systems in place to help you navigate this challenging journey:
- Treatment Options: Work closely with your healthcare team to explore treatment options, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies.
- Support Groups: Joining a lung cancer support group can provide emotional support and valuable insights from others facing similar challenges.
- Nutritional Guidance: Consult with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that supports your health during treatment.
- Emotional Support: Seek counseling or therapy to address the emotional impact of a lung cancer diagnosis.
Remember that you are not alone in your battle against lung diseases. Reach out to healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones for assistance and encouragement.
XV. The Importance of Lung Health for Athletes
For athletes, lung health is of utmost importance, as it directly impacts physical performance and endurance. Athletes rely on their lungs to deliver oxygen to working muscles efficiently. Here are specific considerations for athletes looking to optimize their lung health:
A. Maximizing Lung Capacity
Athletes should focus on maximizing their lung capacity through proper breathing techniques, aerobic conditioning, and strength training. Strategies for athletes include:
- Interval Training: Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to challenge lung capacity and improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Altitude Training: Training at high altitudes can stimulate the production of red blood cells and improve the body’s ability to use oxygen.
- Breathing Drills: Practice breathing exercises to enhance diaphragmatic strength and lung capacity.
B. Managing Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction (EIB)
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, also known as exercise-induced asthma, is a common issue among athletes. It can cause coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath during or after physical activity. Athletes can manage EIB by:
- Using Bronchodilators: Some athletes may benefit from using bronchodilator medications before exercise to prevent EIB symptoms.
- Warming Up: Engage in a thorough warm-up routine before intense workouts or competitions to acclimate the lungs to increased airflow.
- Staying Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain optimal lung function during exercise.
C. Recognizing the Signs of Overtraining
Overtraining can lead to decreased lung function and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. Athletes should be vigilant about recognizing the signs of overtraining, including fatigue, decreased performance, and increased susceptibility to illness.
D. Balancing Rest and Training
Rest and recovery are integral to maintaining lung health for athletes. Adequate sleep and rest days allow the body, including the respiratory system, to recover and adapt to training demands.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
XVI. Respiratory Health in Children
Children’s lung health is of paramount importance as it directly impacts their growth, development, and overall well-being. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in ensuring that children have healthy lungs.
A. Avoiding Secondhand Smoke Exposure
Protecting children from secondhand smoke is essential. Exposure to tobacco smoke increases the risk of respiratory infections, asthma, and other lung-related issues. Ensure that smoking is not allowed in the home or car, and create a smoke-free environment for your child.
B. Promoting Active Play and Exercise
Encourage children to engage in physical activities and play outdoors regularly. Physical activity not only supports healthy lung development but also boosts overall fitness.
C. Maintaining a Nutrient-Rich Diet
Provide children with a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Proper nutrition supports lung health and immune function.
D. Immunizations and Preventive Measures
Follow recommended immunization schedules to protect children from respiratory infections like influenza and pneumonia. Additionally, teach children proper handwashing and respiratory hygiene to prevent the spread of illnesses.
E. Recognizing Allergy and Asthma Symptoms
Be vigilant for signs of allergies or asthma in children, such as frequent coughing, wheezing, or difficulty breathing. If you suspect respiratory issues, consult a pediatrician for evaluation and guidance.
F. Creating a Smoke-Free Home Environment
Ensure that the home environment is free from indoor air pollutants, including smoke, allergens, and pollutants that can affect children’s respiratory health. Proper ventilation and air purification can help maintain clean indoor air.
XVII. Aging and Lung Health
As individuals age, lung health becomes an increasingly important aspect of overall well-being. Aging is associated with natural changes in lung function, but proactive measures can help maintain respiratory health.
A. Age-Related Lung Changes
Aging can lead to several age-related changes in the respiratory system:
- Reduced Lung Elasticity: Lung tissue becomes less elastic, making it harder to exhale completely.
- Weaker Respiratory Muscles: The muscles involved in breathing may weaken, leading to reduced lung capacity.
- Decreased Cough Reflex: The ability to clear mucus from the airways may decline, increasing the risk of respiratory infections.
B. Strategies for Healthy Aging
To promote healthy aging and maintain strong lungs:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercises and strength training, can help counteract age-related changes in lung function.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture supports optimal lung expansion and efficient breathing.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration helps keep mucus in the airways thin and facilitates its removal.
- Lung Health Screenings: Consider lung health screenings, such as spirometry, to monitor lung function as you age.
- Immunizations: Continue to receive recommended vaccinations to protect against respiratory infections.
Proactive measures can contribute to healthy aging and ensure that lung health remains a priority as individuals grow older.
XVIII. Conclusion: A Lifelong Commitment to Lung Health
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
Your lungs are not only essential for the simple act of breathing but also for supporting your overall health and well-being. Strong lungs are the foundation of a robust and active life, whether you’re an athlete seeking peak performance, an individual managing a respiratory condition, or someone committed to a healthy and fulfilling lifestyle.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the intricate anatomy of the lungs, common lung problems, lifestyle factors affecting lung health, breathing techniques, exercise strategies, air quality considerations, natural remedies, medical interventions, and the importance of emotional well-being. We’ve discussed the unique needs of athletes, children, and individuals in different stages of life.
Your lung health is a lifelong commitment, and the choices you make today can have a profound impact on your future well-being. Whether you’re taking steps to quit smoking, incorporating lung-strengthening exercises into your routine, or seeking support for a respiratory condition, remember that you are in control of your lung health journey.
By prioritizing lung health, you are investing in a future filled with vitality, endurance, and the freedom to fully engage in the activities and experiences that bring you joy and fulfillment.
As you embark on this journey, consult with healthcare professionals, seek the support of loved ones, and stay informed about the latest advancements in respiratory care. Your lungs are your lifelong companions, and with the right care and attention, they will continue to support you in every breath you take.
Breathe deeply, live fully, and cherish your lung health—today and for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
1. What are the common signs of unhealthy lung function?
- Learn about the warning signs that may indicate issues with your lung health, such as persistent coughing or shortness of breath.
2. How can I improve my lung capacity and endurance for physical activities?
- Discover effective strategies and exercises that athletes can use to enhance their lung capacity and overall performance.
3. What are some natural remedies for improving lung health?
- Explore natural approaches to boost lung health, including dietary choices, breathing exercises, and steam inhalation.
4. How can I protect my children’s lungs and promote healthy development?
- Find out what steps parents can take to ensure their children grow up with strong and healthy lungs.
5. What are the best practices for quitting smoking and improving lung health?
- Get insights into effective methods for quitting smoking and the benefits of doing so for your lung health.
6. What role does diet play in maintaining strong lungs?
- Understand the impact of nutrition on lung health and discover the foods that can help support your respiratory system.
7. How can I manage exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB)?
- Learn about strategies to prevent and manage exercise-induced asthma symptoms during physical activities.
8. What are the key steps in creating a smoke-free home environment?
- Find practical tips for maintaining clean indoor air and protecting your family from secondhand smoke exposure.
9. How do age-related changes affect lung health, and what can I do to mitigate them?
- Explore the natural changes that occur in the lungs as you age and strategies to maintain healthy respiratory function.
10. What are the latest advancements in lung care and treatment options? – Stay informed about cutting-edge treatments and interventions for various lung conditions and diseases.
How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide
These FAQs provide valuable insights into various aspects of lung health and can help readers better understand and navigate the topic.
1 thought on “How to Make Your Lungs Strong: 1 Comprehensive Guide”