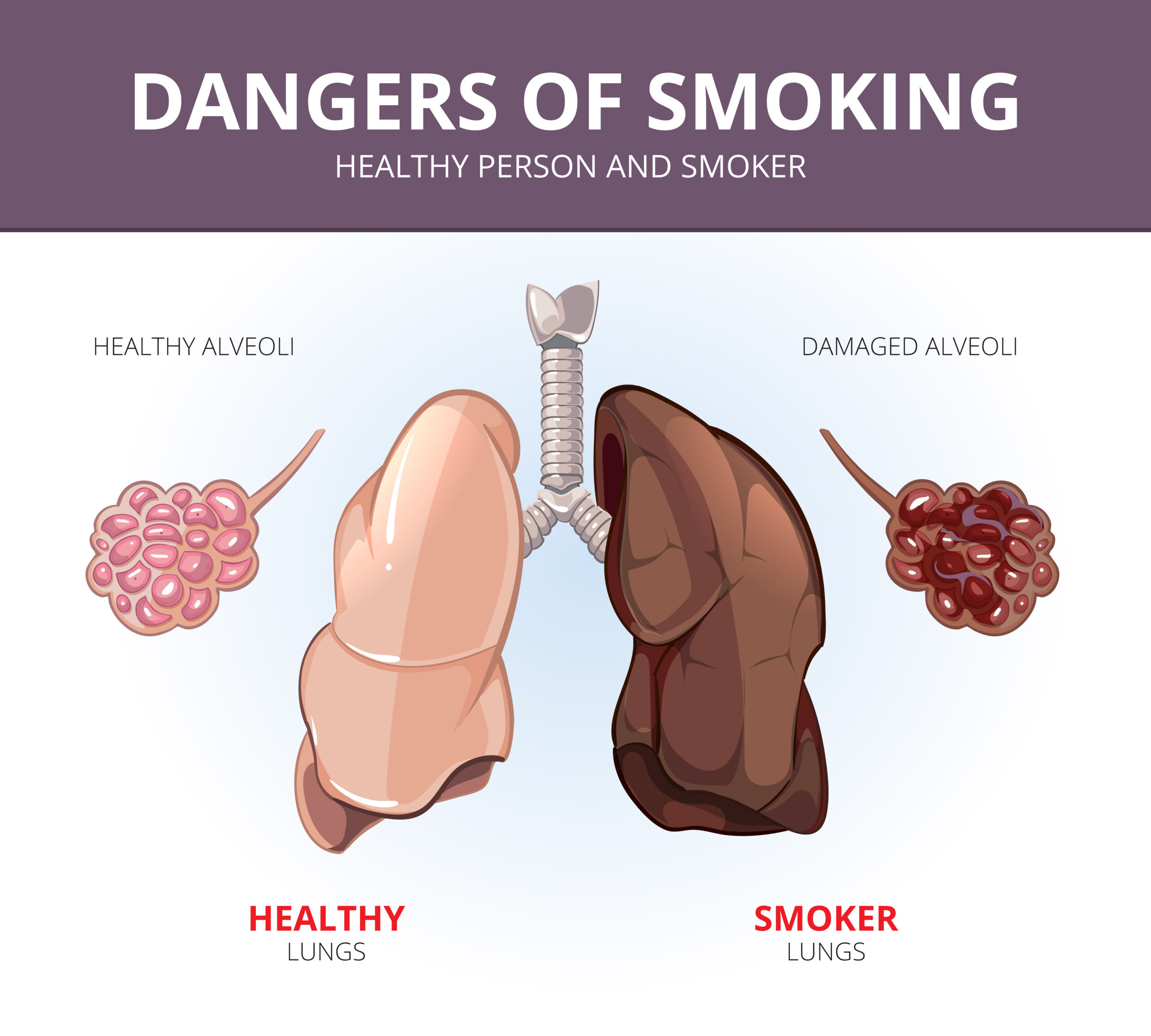
Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Smoking has long been recognized as one of the most detrimental habits to one’s health. It not only affects the overall well-being of an individual but also wreaks havoc on the respiratory system, specifically the lungs. Healthy lungs, on the other hand, are a testament to the body’s remarkable ability to function optimally when not exposed to harmful toxins. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the stark differences between smoker lungs and healthy lungs. From the anatomy to function, and the long-term consequences of smoking, every aspect will be scrutinized. So, let’s take a breath and embark on this enlightening journey.
Table of Contents
Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
I. Introduction
A. The Importance of Healthy Lungs
Healthy lungs are the unsung heroes of our bodies. They work silently and efficiently to ensure that every cell in our system receives the oxygen it needs to function optimally. Without healthy lungs, life as we know it would cease to exist. Their significance cannot be overstated.
B. The Prevalence of Smoking
Despite the well-documented risks and detrimental effects, smoking remains a prevalent habit worldwide. Millions of individuals continue to light up, unaware of the damage they are causing to their lungs and overall health. Understanding the differences between smoker lungs and healthy lungs is crucial to raising awareness about the dangers of smoking.
II. Anatomy of Lungs
A. Healthy Lungs
1. The Structure of Healthy Lungs
Healthy lungs are characterized by their remarkable structure. They consist of two main parts: the left lung and the right lung, both of which are further divided into lobes. The right lung has three lobes, while the left lung has two. This division allows for efficient oxygen exchange.
2. Alveoli: The Oxygen Exchange Units
Within the lobes of healthy lungs lie millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli. These alveoli are where the magic of oxygen exchange takes place. Oxygen from the air we breathe enters the bloodstream through the thin walls of the alveoli, while carbon dioxide, a waste product, is expelled from the body.
3. The Role of Bronchi and Bronchioles
To reach the alveoli, air must pass through a network of airways known as bronchi and bronchioles. These airways are responsible for ensuring that air is distributed evenly to all parts of the lungs. In healthy lungs, this process functions seamlessly.
4. The Pleura: Protecting the Lungs
The pleura is a delicate, two-layered membrane that encases the lungs. It provides protection and lubrication, allowing the lungs to expand and contract smoothly during the breathing process. Healthy lungs benefit from this protective layer.
B. Smoker Lungs
1. Effects of Smoking on Lung Structure
Smoking has a profound and detrimental impact on the structure of the lungs. Over time, exposure to the toxins in cigarette smoke leads to significant changes in lung tissue. These changes include inflammation, scarring, and the accumulation of harmful substances.
2. Tar Buildup: A Sticky Situation
One of the most harmful components of cigarette smoke is tar. Tar is a sticky, brown substance that coats the airways and alveoli of the lungs. This buildup obstructs airflow and impairs the lung’s ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide effectively.
3. Scar Tissue Formation
Chronic smoking leads to the formation of scar tissue within the lungs. This scar tissue, known as fibrosis, further hampers lung function. It reduces the elasticity of the lungs and makes it increasingly difficult to breathe.
4. Reduced Elasticity
Healthy lungs are highly elastic, allowing them to expand and contract with ease during each breath. Smoker lungs, however, lose this elasticity over time. This loss of elasticity is a hallmark of lung damage caused by smoking.

Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
III. Functionality of Lungs
A. Healthy Lungs
1. Efficient Oxygen Exchange
The primary function of healthy lungs is to facilitate efficient oxygen exchange. When we inhale, fresh air filled with oxygen enters the alveoli. These oxygen molecules then pass through the alveolar walls and into the bloodstream, where they are transported to every cell in the body. This process ensures that our organs and tissues receive the oxygen they need to function optimally.
2. The Role of Cilia
Healthy lungs are equipped with tiny hair-like structures called cilia. These cilia line the airways and act as a natural defense mechanism. They help to trap and remove particles, such as dust and bacteria, that may enter the lungs with the inhaled air. This role is vital in maintaining lung health.
3. Lung Capacity and Its Significance
Another crucial aspect of healthy lung functionality is lung capacity. Lung capacity refers to the volume of air that the lungs can hold. Individuals with healthy lungs typically have a higher lung capacity, allowing them to take deep breaths and engage in physical activities without feeling breathless.
B. Smoker Lungs
1. Impaired Oxygen Exchange
Smoking has a profound impact on the ability of the lungs to facilitate oxygen exchange. The buildup of tar and the damage to the alveoli mean that less oxygen can enter the bloodstream. This leads to reduced oxygen levels in the body, which can result in fatigue and shortness of breath.
2. Cilia: Paralyzed and Ineffective
Cigarette smoke paralyzes and damages the cilia in the airways of smoker lungs. Without the protective action of cilia, harmful particles and pathogens can penetrate deeper into the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory infections and illnesses.
3. Decreased Lung Capacity
Smoker lungs exhibit a decrease in lung capacity compared to healthy lungs. This reduced lung capacity can manifest as a persistent feeling of breathlessness, even during mild physical activities. It severely limits the individual’s ability to engage in exercise and other strenuous tasks.
IV. Common Conditions Associated with Smoking
A. Lung Cancer
1. Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is widely recognized as one of the most notorious and life-threatening outcomes of smoking. There are two primary types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Both types can be directly attributed to smoking.
2. Smoking as a Leading Cause
Around the globe, smoking stands as the primary factor behind the development of lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, including carcinogens, initiate changes in lung tissue that can lead to the development of cancerous tumors. Lung cancer is infamous for its devastatingly high death rate.
B. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
1. COPD Explained
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD, is a collective term for a group of progressive lung diseases, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These diseases share common characteristics such as airflow obstruction and breathing difficulties.
2. Smoking’s Contribution to COPD
Smoking is the primary cause of COPD. The toxic substances in cigarette smoke irritate and inflame the airways, leading to chronic bronchitis. Additionally, smoking destroys the alveoli, resulting in emphysema. Together, these conditions make breathing increasingly challenging for individuals with COPD.
Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
V. The Impact on Respiratory Health
A. Respiratory Infections
1. Vulnerability of Smokers
Smokers are more susceptible to respiratory infections than individuals with healthy lungs. The compromised lung function and weakened immune system make it easier for viruses and bacteria to invade the respiratory tract. This heightened vulnerability can lead to frequent illnesses such as colds, flu, and pneumonia.
2. Healthy Lungs’ Defense Mechanisms
Healthy lungs are equipped with robust defense mechanisms that help fend off respiratory infections. The presence of cilia, mucous production, and an efficient immune response all contribute to protecting the respiratory system from pathogens.
B. Asthma
1. Smoking and Asthma
Smoking exacerbates the symptoms of asthma, a chronic respiratory condition characterized by airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can trigger asthma attacks and worsen the condition of asthmatic individuals.
2. Maintaining Healthy Lungs for Asthma Patients
Individuals with asthma benefit greatly from maintaining healthy lungs. Healthy lungs are better equipped to handle the challenges posed by asthma and can minimize the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
VI. Aging Gracefully: Healthy Lungs vs. Smoker Lungs
A. Lung Aging Process
1. The Natural Aging of Lungs
As individuals age, their lungs naturally undergo changes. Lung tissue becomes less elastic, and lung capacity may decrease slightly. However, these age-related changes are typically gradual and do not significantly impact overall lung function.
2. Accelerated Aging Due to Smoking
In contrast, smoking accelerates the aging process of the lungs. Smoker lungs exhibit signs of premature aging, with a marked decrease in elasticity and lung capacity. This accelerated aging contributes to the development of respiratory conditions and a decreased quality of life.
B. Implications for the Elderly
1. Quality of Life
Elderly individuals with smoker lungs often experience a lower quality of life compared to those with healthy lungs. They may struggle with daily activities and face an increased risk of respiratory illnesses and complications.
2. Treatment Challenges
Treating respiratory conditions in the elderly with smoker lungs can be particularly challenging. The damage caused by smoking may limit treatment options, making it imperative to prioritize lung health from a young age.

Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
VII. Secondhand Smoke: A Silent Threat
A. Understanding Secondhand Smoke
1. Passive Smoking
While the focus has primarily been on the impact of smoking on the individual smoker, secondhand smoke is a significant concern. Passive smoking, or involuntary exposure to cigarette smoke, poses serious health risks to non-smokers.
2. Effects on Non-Smokers
Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke can experience many of the same health problems as active smokers. This includes an increased risk of respiratory infections, asthma exacerbations, and even lung cancer. Ensuring the safety of non-smokers from secondhand smoke is vital for the overall well-being of the public.
B. Protecting Loved Ones
1. Creating Smoke-Free Environments
To safeguard the health of loved ones, it is crucial to create smoke-free environments. Implementing smoking bans in homes and public spaces helps reduce exposure to secondhand smoke and its associated health risks.
2. Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about the dangers of secondhand smoke is an essential step in protecting non-smokers. Education campaigns and advocacy efforts can help reduce the prevalence of smoking and its impact on society.
VIII. The Road to Recovery
A. Smoking Cessation
1. Strategies to Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is the most effective way to halt further damage to smoker lungs. There are various strategies and resources available to help individuals quit smoking, including nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, and support groups.
2. Support Systems
A strong support system is often instrumental in successfully quitting smoking. Friends, family, and healthcare professionals can provide encouragement and assistance throughout the journey to become smoke-free.
B. Lung Rehabilitation
1. Regaining Lung Health
For those with smoker lungs, lung rehabilitation programs can be immensely beneficial. These programs incorporate exercises, breathing techniques, and education to improve lung function and overall well-being.
2. Exercises and Therapies
Specific exercises and therapies can help individuals with smoker lungs regain some lost lung function. These may include pulmonary rehabilitation exercises, breathing exercises, and medications to manage symptoms.

Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
IX. Future Perspectives
A. Advances in Lung Health
1. Medical Breakthroughs
The field of lung health is continually advancing, with ongoing research leading to medical breakthroughs. New treatments and therapies offer hope for individuals with damaged lungs, including those caused by smoking.
2. Technological Innovations
Technological innovations such as lung transplantation and artificial lung development are on the horizon. These advancements hold the promise of improving the lives of individuals with severe lung damage.
B. Promoting a Smoke-Free World
1. Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in reducing smoking rates and protecting lung health. Governments and organizations worldwide are implementing policies to discourage smoking and promote smoke-free environments.
2. Education and Awareness
Education remains a powerful tool in the fight against smoking. Raising awareness about the risks and consequences of smoking is essential for preventing new smokers and supporting those on their journey to quit.
X. Conclusion:
Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
A. A Tale of Two Lungs
The comparison between smoker lungs and healthy lungs is a stark reminder of the profound impact of smoking on respiratory health. While healthy lungs facilitate efficient oxygen exchange and protect against respiratory infections, smoker lungs endure irreversible damage that can lead to life-threatening conditions.
B. The Power of Choice
Ultimately, the choice to smoke or not lies in the hands of individuals. Understanding the stark contrast between smoker lungs and healthy lungs serves as a powerful motivator for making informed decisions about one’s health. Quitting smoking and prioritizing lung health can lead to a brighter and healthier future.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs: Unveiling the Hidden 9 Truth
Q1. What are the key differences between smoker lungs and healthy lungs?
A1. Smoker lungs and healthy lungs differ in terms of structure, function, and health outcomes. Smoker lungs often exhibit damage, reduced elasticity, and increased susceptibility to diseases like lung cancer and COPD, whereas healthy lungs are characterized by efficient oxygen exchange and better defense mechanisms.
Q2. How does smoking impact lung health?
A2. Smoking exposes the lungs to harmful toxins and chemicals found in cigarette smoke. Over time, this leads to inflammation, tar buildup, scar tissue formation, and a decrease in lung capacity. Smoking is also a leading cause of lung cancer and COPD.
Q3. Can smoker lungs recover if someone quits smoking?
A3. While quitting smoking can halt further damage to the lungs, it’s essential to note that some damage may be irreversible. However, lung rehabilitation programs, lifestyle changes, and medical support can help individuals with smoker lungs improve their lung function and overall health.
Q4. What are the common respiratory conditions associated with smoking?
A4. Smoking is strongly linked to lung cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), which includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions are major health risks for smokers.
Q5. How can individuals protect themselves from secondhand smoke?
A5. Protecting oneself from secondhand smoke involves creating smoke-free environments, especially in homes and public spaces. Raising awareness about the dangers of secondhand smoke and advocating for smoke-free policies is also crucial.
Q6. Are there any recent advancements in lung health treatments?
A6. Yes, there have been significant advancements in lung health treatments. These include medical breakthroughs, such as innovative therapies and treatments for lung diseases. Additionally, there are ongoing developments in technologies like lung transplantation and artificial lung development.
Q7. What can individuals do to maintain healthy lungs?
A7. To maintain healthy lungs, individuals should prioritize not smoking, avoid exposure to environmental toxins, engage in regular physical activity, maintain a balanced diet, and take precautions against respiratory infections.
Q8. Can the natural aging process impact lung health?
A8. Yes, as individuals age, their lung function naturally changes, with a slight decrease in lung elasticity and capacity. However, smoking accelerates this aging process, leading to more significant declines in lung health.
Q9. How can one quit smoking successfully?
A9. Quitting smoking is challenging but possible. Strategies include seeking professional help, using nicotine replacement therapy, joining support groups, and setting a quit date. Having a strong support system and motivation are also key factors in successful quitting.
Q10. What is the significance of lung capacity in overall health?
A10. Lung capacity is vital for overall health as it determines how efficiently oxygen is delivered to the body’s cells. Higher lung capacity allows for better physical performance and a reduced risk of breathlessness during activities.
These FAQs provide additional information and address common queries that readers may have after reading the blog post on “Smoker Lungs vs Healthy Lungs.”