I. Introduction
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, may seem inconspicuous, but its influence on the human body is profound. Often referred to as the “master regulator of metabolism,” the thyroid plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. This comprehensive article delves into the intricate world of the thyroid, from its anatomy and function to the various disorders that can affect it. We will explore topics ranging from thyroid nodules and cancer to the impact of thyroid health on metabolism, mental health, and more. Join us on this journey to unravel the mysteries of the thyroid gland.
Table of Contents
II. Anatomy of the Thyroid
Thyroid Location and Structure
The thyroid gland resides just below the Adam’s apple, wrapped around the front of the windpipe. Its position allows it to efficiently regulate essential bodily functions.
The thyroid consists of two lobes connected by a bridge called the isthmus. This unique structure resembles a butterfly with its wings outstretched. Understanding this anatomy is crucial to comprehend its functions.
Thyroid Hormones: T3, T4, and Calcitonin
The thyroid gland produces three primary hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. These hormones serve distinct roles in maintaining bodily equilibrium.
T4 is the inactive form of thyroid hormone and is converted into the active T3 in various tissues. Calcitonin, although less known, plays a role in calcium regulation.
The Pituitary-Thyroid Axis
The thyroid’s activity is not autonomous. It operates under the regulation of the pituitary gland, which secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The interaction between the pituitary and thyroid glands is a delicate feedback loop that maintains hormonal balance.
III. Thyroid Disorders
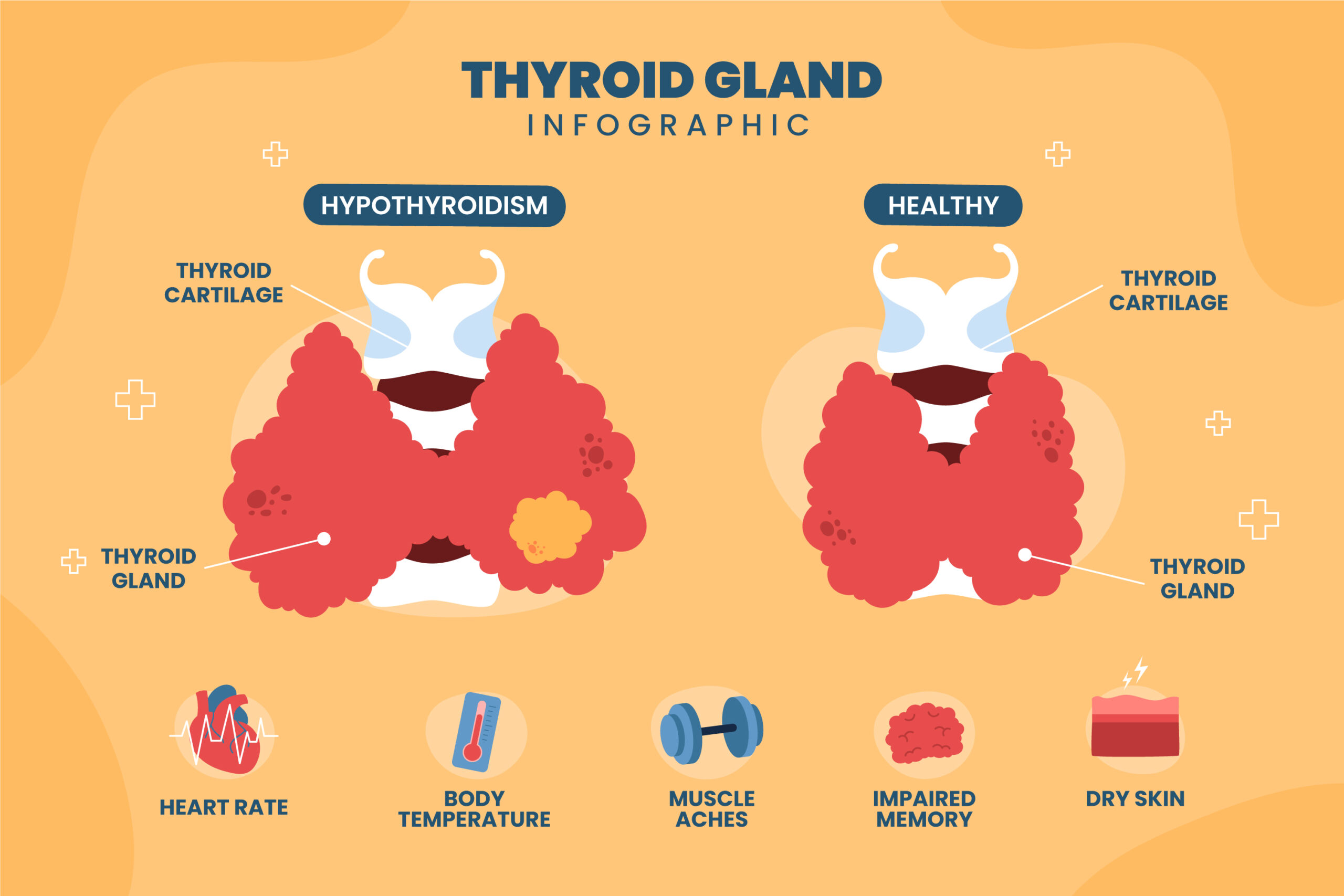
Hypothyroidism
Causes and Risk Factors
Hypothyroidism, often referred to as an underactive thyroid, occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient hormones. Several factors contribute to its development, including autoimmune conditions, medications, and iodine deficiency.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of hypothyroidism are diverse, often mirroring other health issues. Diagnosis relies on blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels and TSH.
Treatment Options
Treatment typically involves synthetic hormone replacement therapy to restore thyroid hormone levels to normal. Lifestyle changes and dietary adjustments may also play a role.
Hyperthyroidism
Causes and Risk Factors
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland becomes overly active, which is the opposite of hypothyroidism where the thyroid is underactive. Causes include autoimmune conditions, thyroid nodules, and excessive iodine intake.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can be more overt, including rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and anxiety. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging.
Treatment Options
Managing hyperthyroidism aims to reduce hormone production. Treatment options range from medications to radioactive iodine therapy and surgery in severe cases.
IV. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Autoimmune Nature of Hashimoto’s
In the United States, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis stands as the leading cause of hypothyroidism. It’s an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
Impact on Thyroid Function
As the immune system damages the thyroid, it becomes less capable of producing hormones. This chronic inflammation leads to the characteristic symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Managing Hashimoto’s
Treatment focuses on replacing thyroid hormones and reducing inflammation. Patients may need lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
V. Graves’ Disease
Autoimmune Origins of Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease, a leading cause of hyperthyroidism, is also autoimmune in nature. The immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid to produce excess hormones.
Overactivity of the Thyroid
The excessive thyroid hormone production leads to a range of symptoms, including weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and goiter (enlarged thyroid gland).
Treatment Approaches for Graves’ Disease
Treatment options include medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, and, in some cases, thyroid surgery.
VI. Thyroid Nodules and Goiter
Types of Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are growths within the thyroid gland. They can be classified as benign (non-cancerous), malignant (cancerous), or indeterminate.
Causes and Symptoms
Nodules can result from various factors, including iodine deficiency and genetic predisposition. Most thyroid nodules are asymptomatic but can cause discomfort or difficulty swallowing when they grow large.
Treatment and Monitoring
The approach to thyroid nodules depends on their type and size. Benign nodules may only require monitoring, while malignant ones may necessitate surgery or other treatments.
VII. Thyroid Cancer
Types of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer can manifest in different forms, with papillary and follicular thyroid cancers being the most common. Medullary and anaplastic thyroid cancers are less prevalent but more aggressive.
Risk Factors
Factors such as radiation exposure, family history, and certain genetic mutations increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis typically involves a biopsy and imaging studies. Treatment may involve surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and sometimes external radiation therapy.
VIII. Thyroid and Metabolism
The Role of Thyroid Hormones in Metabolism
Thyroid hormones play a central role in regulating metabolism, affecting processes like energy production, temperature regulation, and weight management.
How Thyroid Disorders Affect Metabolism
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt metabolic balance. Hypothyroidism often leads to weight gain, while hyperthyroidism may cause weight loss.
Weight Management and Thyroid Health
Balancing thyroid hormones is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Proper treatment and lifestyle choices can help manage weight effectively.
IX. Diet and Lifestyle for Thyroid Health
Nutrients Essential for Thyroid Function
Several nutrients, including iodine, selenium, and zinc, are vital for optimal thyroid function. A balanced diet is essential to ensure these nutrients are readily available.
Foods to Support Thyroid Health
Certain foods, such as iodized salt, seafood, and Brazil nuts, can support thyroid health by providing essential nutrients.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular physical activity and effective stress management techniques can help support thyroid function and overall well-being.
X. Thyroid Function Testing
Blood Tests for Thyroid Function
Blood tests, including TSH, T3, and T4 measurements, are essential for assessing thyroid function. These tests provide valuable insights into thyroid health.
Interpreting Thyroid Function Results
Understanding the results of thyroid function tests is crucial for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders effectively.
Monitoring Thyroid Health
Individuals with thyroid conditions must undergo regular monitoring to ensure their treatment remains effective and their thyroid hormones are balanced.
XI. Pregnancy and Thyroid Health
Thyroid Function During Pregnancy
Pregnancy places additional demands on the thyroid gland. Proper thyroid function is crucial for both the mother’s health and the baby’s development.
Impact on Fetal Development
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in developing the fetal brain and nervous system. Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can lead to complications.
Managing Thyroid Health During Pregnancy
Pregnant individuals with thyroid conditions should work closely with healthcare providers to manage their thyroid health and reduce potential risks.
XII. Thyroid Supplements and Medications
Common Thyroid Medications
Synthetic thyroid hormones like levothyroxine are commonly prescribed to manage hypothyroidism. These medications aim to restore normal hormone levels.
Use of Natural Thyroid Supplements
Some individuals explore natural supplements like iodine or herbal remedies to support thyroid health. It’s essential to use these with caution and under medical supervision.
Risks and Benefits
Understanding the potential risks and benefits of thyroid medications and supplements is crucial for making informed treatment choices.
XIII. Thyroid Health in Aging
Age-Related Changes in Thyroid Function
Thyroid function can change with age, often resulting in a decline in hormone production. These age-related changes can impact overall health.
Managing Thyroid Health as You Age
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying active, and maintaining a balanced diet are essential for managing thyroid health as you age.
XIV. Thyroid and Mental Health
Thyroid Disorders and Mood
Thyroid disorders can significantly affect mood, leading to symptoms of depression, anxiety, or even cognitive impairment.
Anxiety and Depression in Thyroid Conditions
Understanding the connection between thyroid function and mental health is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Treating Mental Health Alongside Thyroid Issues
Addressing mental health concerns alongside thyroid treatment can lead to improved overall well-being and quality of life.
XV. Thyroid and Hair Loss
Connection Between Thyroid and Hair Health
Thyroid function plays a vital role in maintaining healthy hair. Disruptions in thyroid hormones can lead to hair loss.
Managing Hair Loss Due to Thyroid Conditions
Various strategies, including medication adjustments and nutritional support, can help manage and potentially reverse thyroid-related hair loss.
When to Seek Help
Individuals experiencing significant hair loss should seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
XVI. Thyroid and Skin
Thyroid Disorders and Skin Issues
Thyroid disorders can manifest in various skin problems, from dryness and pallor to hair texture changes.
Skin Care for People with Thyroid Conditions
Proper skincare and dermatological care can help manage skin issues associated with thyroid disorders.
Dermatological Concerns
Specific dermatological concerns, such as pretibial myxedema and vitiligo, are associated with thyroid dysfunction and require specialized treatment.
XVII. Thyroid and Heart Health
Influence of Thyroid Hormones on Heart Function
Thyroid hormones have a significant impact on heart rate, rhythm, and overall cardiovascular health.
Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can lead to cardiovascular issues, including high blood pressure and an increased risk of heart disease.
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention
Preventing cardiovascular complications involves effective management of thyroid disorders and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
XVIII. Thyroid and Bone Health
Thyroid Hormones and Bone Density
Thyroid hormones are essential for maintaining bone density. Hormonal imbalances can lead to conditions like osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis and Thyroid Conditions
Individuals with thyroid disorders, particularly hyperthyroidism, are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis. Preventive measures are essential.
Strategies for Maintaining Bone Health
Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, weight-bearing exercise, and appropriate medical interventions, can help maintain strong and healthy bones.
XIX. Thyroid and Reproductive Health
Thyroid Disorders and Fertility
Thyroid disorders can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting fertility in both men and women. Proper management is vital for those planning to conceive.
Pregnancy Complications Linked to Thyroid Issues
Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can lead to complications for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Managing Reproductive Health
Working closely with healthcare providers to manage thyroid health is crucial for individuals planning to start or expand their families.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k77F184hi5g
XX. Conclusion
The thyroid gland, often underestimated in its significance, holds the key to a multitude of bodily functions. From regulating metabolism to impacting mental health, skin, hair, and the heart, its influence is far-reaching. Understanding the complexities of thyroid health is essential for overall well-being. By staying informed, seeking appropriate medical care, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals can empower themselves to maintain optimal thyroid health. The journey through the intricacies of the thyroid gland has revealed its critical role as the master regulator of metabolism, and it is now in your hands to ensure its well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is the thyroid, and where is it located in the body?
- The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, wrapped around the front of the windpipe.
2. What are the main hormones produced by the thyroid, and what are their functions?
- The thyroid gland produces three primary hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. T4 and T3 play crucial roles in regulating metabolism, while calcitonin is involved in calcium regulation.
3. What are the common thyroid disorders, and what are their symptoms?
- Common thyroid disorders include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Symptoms vary but can include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and more.
4. How are thyroid disorders diagnosed?
- Thyroid disorders are typically diagnosed through blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. Imaging studies may also be used for further evaluation.
5. What are the treatment options for thyroid disorders?
- Treatment depends on the specific thyroid disorder. Hypothyroidism is often treated with synthetic hormone replacement therapy, while hyperthyroidism may involve medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
6. What is the relationship between the immune system and thyroid health?
- There is a complex relationship between the immune system and the thyroid. Certain autoimmune conditions, like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the thyroid gland.
7. How can diet and lifestyle affect thyroid health?
- A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like iodine and selenium is crucial for maintaining thyroid health. Lifestyle factors, such as stress management and exercise, can also have a significant impact.
8. Are there any emerging trends in thyroid care and research?
- Yes, ongoing research is exploring personalized medicine in thyroid care, technological advancements in diagnosis and treatment, and the potential link between thyroid health and longevity.
9. What are some common myths and misconceptions about thyroid health?
- Common myths include beliefs about iodine, diet, and thyroid disorders. It’s important to separate fact from fiction for better understanding.
10. How can individuals with thyroid disorders lead a healthy life?
- Living with a thyroid disorder may involve coping strategies, support networks, and adherence to treatment plans. Proper education and self-care are essential.
11. Is there a connection between environmental factors and thyroid health?
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants, can impact thyroid health and contribute to thyroid disorders. Adopting protective measures is crucial.
12. What does the future hold for thyroid care and management?
- The future of thyroid care includes advancements in technology, personalized medicine, preventive measures, and ongoing research to improve diagnosis and treatment.
These FAQs provide valuable insights into thyroid health and can help readers navigate the complex world of thyroid disorders and care.
1 thought on “Thyroid: 15+ Healthy Ways Understanding the Master Regulator of Metabolism | 1 Comprehensive Guide”